How to Serve a Node App in Docker
Nick Scialli
October 17, 2020
Serving a node application in Docker is actually fairly simply. In this post, we’ll do so using only a six-line Dockerfile!
Create a Sample App
For our proof-of-concept, we’ll create a sample node app in a new directory. Let’s quickly put one together.
Create app directory
First create a node-in-docker directory and cd into it.
mkdir node-in-docker
cd node-in-dockerinitialize npm project with defaults
Next, initialize an npm project. The -y flag will initilize with default settings.
npm init -yAdd express.js and simple code
Our app will be an express app.
npm i expressCreate an index.js file with some simple home route handling.
touch index.jsWith the following code:
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const port = process.env.NODE_SERVER_PORT;
app.get('/', (req, res) => res.send('Sample node app!'));
app.listen(port, () =>
console.log(`Example app listening at http://localhost:${port}`)
);Note that our port will come from a NODE_SERVER_PORT environment variable.
Test the app
Let’s test that our app looks good before we add any Docker code. We can do this by using node . and remembering to include our environment variable.
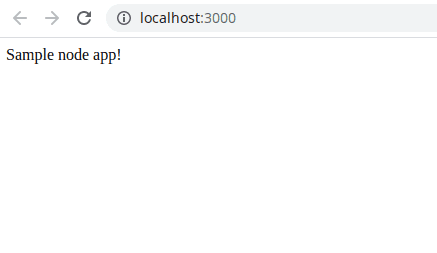
NODE_SERVER_PORT=3000 node .Now if we navigate to http://localhost:3000, we should see our sample app.
If you see this, we’re now ready to dive into docker land!
Add Docker
In this minimal example, all we’ll need is two files:
- Dockerfile
- .dockerignore
The Dockerfile will be the blueprint for creating our Docker image and the .dockerignore will be used to tell Docker to ignore the node_modules folder when building the image.
.dockerignore
The .dockerignore file is pretty easy, let’s just throw the string node_modules in there.
echo "node_modules" > .dockerignoreDockerfile
The Dockerfile is a bit more complex, but not by much!
Let’s first create the file
touch DockerfileAnd now here’s the magic. Read the comments to see what’s going on.
# Use the node v10 image
FROM node:10
# Set working directory
WORKDIR /app
# Copy contents of current directory into working dir
COPY . .
# install node modules
RUN npm i
# Set the node server port to 3000
ENV NODE_SERVER_PORT=3000
# Containers start the app by running node .
ENTRYPOINT ["node", "."]Build the Docker image
Let’s build the docker image based on the instructions in our Dockerfile!
We will use the tag (-t) node-server and our build context will be the current directory (.).
docker build -t node-server .Run a container
Now we can create and run a container based on our node-server image! To so so, we’ll use the following options:
--rmto cleanup old instances-itflags for terminal behavior- Expose container port 3000 on port 3000
docker run --rm -it -p 3000:3000 node-serverNow if everything works, we should be able to go to http://localhost:3000 and see our sample node app!

Nick Scialli is a senior UI engineer at Microsoft.